本笔记主要记录lwip框架部分,目的是为了对lwip的源码实现有初步了解,方便后面细节分析。
参考:
协议栈初始化lwip_init()在init.c文件中。
如果移植入带系统的工程中,则调用tcpip_init():
lwip_init()进行内核初始化。tcpip_thread中跑。tcpip_mbox邮箱,成员个数为TCPIP_MBOX_SIZE。主要用于接收从底层或者上层传递过来的消息。lock_tcpip_core内核锁。tcpip_thread线程。这个线程就是LwIP在操作系统中作为一个独立的线程运行,所有处理的数据都要这个线程去处理。/** * @ingroup lwip_os * Initialize this module: * - initialize all sub modules * - start the tcpip_thread * * @param initfunc a function to call when tcpip_thread is running and finished initializing * @param arg argument to pass to initfunc */voidtcpip_init(tcpip_init_done_fn initfunc, void *arg){ lwip_init(); tcpip_init_done = initfunc; /* 初始化后的钩子函数 */ tcpip_init_done_arg = arg; /* 初始化后的钩子函数的参数 */ /* 创建内核邮箱 */ if (sys_mbox_new(&tcpip_mbox, TCPIP_MBOX_SIZE) != ERR_OK) { LWIP_ASSERT("failed to create tcpip_thread mbox", 0); }#if LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING /* 创建内核锁 */ if (sys_mutex_new(&lock_tcpip_core) != ERR_OK) { LWIP_ASSERT("failed to create lock_tcpip_core", 0); }#endif /* LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING */ /* 创建内核线程 */ sys_thread_new(TCPIP_THREAD_NAME, tcpip_thread, NULL, TCPIP_THREAD_STACKSIZE, TCPIP_THREAD_PRIO);}如果在裸机中,可以直接调用lwip_init()。
lwip_init()在init.c文件中。
lwip_init()源码:
lwip_init(),否则,用户只能调用tcpip_init()来实现初始化,但是最终都是会调用到lwip_init()函数。/** * @ingroup lwip_nosys * Initialize all modules. * Use this in NO_SYS mode. Use tcpip_init() otherwise. */voidlwip_init(void){#ifndef LWIP_SKIP_CONST_CHECK int a = 0; LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(a); LWIP_ASSERT("LWIP_CONST_CAST not implemented correctly. Check your lwIP port.", LWIP_CONST_CAST(void *, &a) == &a);#endif#ifndef LWIP_SKIP_PACKING_CHECK LWIP_ASSERT("Struct packing not implemented correctly. Check your lwIP port.", sizeof(struct packed_struct_test) == PACKED_STRUCT_TEST_EXPECTED_SIZE);#endif /* Modules initialization */ stats_init();#if !NO_SYS sys_init();#endif /* !NO_SYS */ mem_init(); memp_init(); pbuf_init(); netif_init();#if LWIP_IPV4 ip_init();#if LWIP_ARP etharp_init();#endif /* LWIP_ARP */#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */#if LWIP_RAW raw_init();#endif /* LWIP_RAW */#if LWIP_UDP udp_init();#endif /* LWIP_UDP */#if LWIP_TCP tcp_init();#endif /* LWIP_TCP */#if LWIP_IGMP igmp_init();#endif /* LWIP_IGMP */#if LWIP_DNS dns_init();#endif /* LWIP_DNS */#if PPP_SUPPORT ppp_init();#endif#if LWIP_TIMERS sys_timeouts_init();#endif /* LWIP_TIMERS */}tcpip协议栈的超时机制也是很重要的一部分。
ARP缓存表项的时间管理、IP分片数据报的重装等待超时、TCP中的建立连接超时、重传超时机制等都会用到。
LwIP为每个与外界网络连接的任务都有设定了timeout属性。
其实现源码主要在timeouts.c和timeouts.h。
内核只有一条超时链表static struct sys_timeo *next_timeout;。
该链表的数据结构是一个有序单向非循环的非通用链表。
把需要超时处理的事件按唤醒时间升序插入到该链表中。
通过sys_timeouts_sleeptime()函数获取下次唤醒的时间,到唤醒的时间后就会通过sys_check_timeouts()遍历next_timeout超时链表。
这个只是底层的内核超时机制,另外lwip还基于这个机制再实现一套周期定时机制。
周期定时机制时基于内核超时机制而实现的。
初始化内核超时机制时,把周期定时函数lwip_cyclic_timer()作为超时函数,lwip_cyclic_timers[]数组保存的回调函数作为lwip_cyclic_timer()的参数,让其周期回调。
因为超时链表next_timeout中的事件超时后会出队,但是lwip_cyclic_timers()函数里面会将自己再次入队,这样实现周期回调。
内核超时链表:
/** The one and only timeout list */static struct sys_timeo *next_timeout;内核超时链表数据结构:
struct sys_timeo { struct sys_timeo *next; /* 下一个节点 */ u32_t time; /* 被唤醒的时间 */ sys_timeout_handler h; /* 回调 */ void *arg; /* 回调的参数 */#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES const char* handler_name; /* 当前超时事件的描述。调试使用 */#endif /* LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES */};初始化内核超时模块:
/** Initialize this module */void sys_timeouts_init(void){ size_t i; /* tcp_tmr() 不用在初始化时就插入延时链表,因为还没用到 */ for (i = (LWIP_TCP ? 1 : 0); i < LWIP_ARRAYSIZE(lwip_cyclic_timers); i++) { /* 把lwip_cyclic_timers数组保存的回调插入到超时链表中 */ sys_timeout(lwip_cyclic_timers[i].interval_ms, lwip_cyclic_timer, LWIP_CONST_CAST(void *, &lwip_cyclic_timers[i])); }}lwip_cyclic_timers数组:
/* 这个数组包含所有堆栈内部的循环计时器 */const struct lwip_cyclic_timer lwip_cyclic_timers[] = {#if LWIP_TCP /* TCP计时器是一种特殊情况:它不必总是运行,初始化内核超时机制时就不会将其插入超时链表。可使用tcp_timer_needed()触发从TCP启动。*/ {TCP_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(tcp_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_TCP */#if LWIP_IPV4#if IP_REASSEMBLY {IP_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(ip_reass_tmr)},#endif /* IP_REASSEMBLY */#if LWIP_ARP {ARP_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(etharp_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_ARP */#if LWIP_DHCP {DHCP_COARSE_TIMER_MSECS, HANDLER(dhcp_coarse_tmr)}, {DHCP_FINE_TIMER_MSECS, HANDLER(dhcp_fine_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_DHCP */#if LWIP_ACD {ACD_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(acd_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_ACD */#if LWIP_IGMP {IGMP_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(igmp_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_IGMP */#endif /* LWIP_IPV4 */#if LWIP_DNS {DNS_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(dns_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_DNS */#if LWIP_IPV6 {ND6_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(nd6_tmr)},#if LWIP_IPV6_REASS {IP6_REASS_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(ip6_reass_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_REASS */#if LWIP_IPV6_MLD {MLD6_TMR_INTERVAL, HANDLER(mld6_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_MLD */#if LWIP_IPV6_DHCP6 {DHCP6_TIMER_MSECS, HANDLER(dhcp6_tmr)},#endif /* LWIP_IPV6_DHCP6 */#endif /* LWIP_IPV6 */};/* lwip_num_cyclic_timers表示lwip_cyclic_timers数组有多少个成员 */const int lwip_num_cyclic_timers = LWIP_ARRAYSIZE(lwip_cyclic_timers);看过freertos内核实现都知道,这个rtos是通过两条延时链表(一条当前延时链表和一条溢出延时链表)来处理延时溢出的。
而lwip内核超时机制就只有一条超时链表,溢出,只能靠其它逻辑判断了。
用TIME_LESS_THAN()宏函数来处理溢出。
/* 首先限制超时最大的差值,这也是单链表溢出处理的局限 */#define LWIP_MAX_TIMEOUT 0x7fffffff/* t比compare_tocompare_to少就返回1,这个对时间节拍溢出也能正确判断。原理我不会文字表达,自己找个例子验证下吧 */#define TIME_LESS_THAN(t, compare_to) ( (((u32_t)((t)-(compare_to))) > LWIP_MAX_TIMEOUT) ? 1 : 0 )我还是举个例子说明下吧:
例子1,正常情况下(时间轴t在c前):t和c比较,c还没溢出,t-c为负,16进制表示为0x8xxxxxxx,比0x7fffffff大,返回1。
例子2,溢出情况下(时间轴t在c前):t和c比较,c溢出,由于限制了c到t的差距必须在LWIP_MAX_TIMEOUT内,t-c的差值一定大于0xFFFFFFFF-LWIP_MAX_TIMEOUTLWIP_MAX_TIMEOUT,还是比0x7fffffff大,返回1。
注册超时事件使用sys_timeout(),内部会调用sys_timeout_abs()把超时事件插入到超时链表next_timeout中。
/** * Create a one-shot timer (aka timeout). Timeouts are processed in the * following cases: * - while waiting for a message using sys_timeouts_mbox_fetch() * - by calling sys_check_timeouts() (NO_SYS==1 only) * * @param msecs time in milliseconds after that the timer should expire * @param handler callback function to call when msecs have elapsed * @param arg argument to pass to the callback function */#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMESvoidsys_timeout_debug(u32_t msecs, sys_timeout_handler handler, void *arg, const char *handler_name)#else /* LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES */voidsys_timeout(u32_t msecs, sys_timeout_handler handler, void *arg)#endif /* LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES */{ u32_t next_timeout_time; /* 确保当前处于TCPIP线程安全锁内 */ LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED(); /* 超时限制 */ LWIP_ASSERT("Timeout time too long, max is LWIP_UINT32_MAX/4 msecs", msecs <= (LWIP_UINT32_MAX / 4)); /* 计算唤醒时间 */ next_timeout_time = (u32_t)(sys_now() + msecs); /* 由TIME_LESS_THAN宏处理溢出 */#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES sys_timeout_abs(next_timeout_time, handler, arg, handler_name);#else /* 把当前超时事件插入到超时链表,成注册 */ sys_timeout_abs(next_timeout_time, handler, arg);#endif}超时事件插入超时链表sys_timeout_abs():
static void#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMESsys_timeout_abs(u32_t abs_time, sys_timeout_handler handler, void *arg, const char *handler_name)#else /* LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES */sys_timeout_abs(u32_t abs_time, sys_timeout_handler handler, void *arg)#endif{ struct sys_timeo *timeout, *t; /* 从内存池中获取内存资源 */ timeout = (struct sys_timeo *)memp_malloc(MEMP_SYS_TIMEOUT); if (timeout == NULL) { LWIP_ASSERT("sys_timeout: timeout != NULL, pool MEMP_SYS_TIMEOUT is empty", timeout != NULL); return; } /* 配置超时事件数据结构 */ timeout->next = NULL; timeout->h = handler; timeout->arg = arg; timeout->time = abs_time;#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES /* 当前超时事件的文本描述 */ timeout->handler_name = handler_name; LWIP_DEBUGF(TIMERS_DEBUG, ("sys_timeout: %p abs_time=%"U32_F" handler=%s arg=%p\n", (void *)timeout, abs_time, handler_name, (void *)arg));#endif /* LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES */ if (next_timeout == NULL) { next_timeout = timeout; /* 如果超时链表没有超时事件,那当前超时事件就作为超时链表的首节点 */ return; } /* 按唤醒时间有序插入 */ if (TIME_LESS_THAN(timeout->time, next_timeout->time)) { /* 当前超时事件被唤醒的时间比超时链表中的所有超时事件都要早,那当前节点就做超时链表的头儿 */ timeout->next = next_timeout; next_timeout = timeout; } else { /* 按唤醒时间把超时事件有序插入到超时链表中 */ for (t = next_timeout; t != NULL; t = t->next) { if ((t->next == NULL) || TIME_LESS_THAN(timeout->time, t->next->time)) { timeout->next = t->next; t->next = timeout; break; } } }}注销超时事件的主要步骤:
/** * Go through timeout list (for this task only) and remove the first matching * entry (subsequent entries remain untouched), even though the timeout has not * triggered yet. * * @param handler callback function that would be called by the timeout * @param arg callback argument that would be passed to handler*/voidsys_untimeout(sys_timeout_handler handler, void *arg){ struct sys_timeo *prev_t, *t; /* 确保在tcpip线程安全锁内 */ LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED(); if (next_timeout == NULL) { return; } for (t = next_timeout, prev_t = NULL; t != NULL; prev_t = t, t = t->next) { if ((t->h == handler) && (t->arg == arg)) { /* 在链表中找到该事件 */ /* 从超时链表中提除 */ if (prev_t == NULL) { next_timeout = t->next; } else { prev_t->next = t->next; } /* 释放内存资源 */ memp_free(MEMP_SYS_TIMEOUT, t); return; } } return;}在裸机中,可以直接定时调用sys_check_timeouts()函数来实现超时检查处理。
在系统中,超时检查处理在tcpip_timeouts_mbox_fetch(sys_mbox_t *mbox, void **msg);函数被调用。
tcpip_timeouts_mbox_fetch()这个函数会在tcpip_thread()被一直调用。主要内容是等待tcpip_mbox消息,是可阻塞的,如果在等待tcpip_mbox的过程中发生超时事件,则会同时执行超时事件处理。
/** * @ingroup lwip_nosys * Handle timeouts for NO_SYS==1 (i.e. without using * tcpip_thread/sys_timeouts_mbox_fetch(). Uses sys_now() to call timeout * handler functions when timeouts expire. * * Must be called periodically from your main loop. */voidsys_check_timeouts(void){ u32_t now; /* 确保在tcpip线程安全锁内 */ LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED(); /* 获取当前时间 */ now = sys_now(); do { /* 把所有已经超时的事件都处理一遍 */ struct sys_timeo *tmptimeout; sys_timeout_handler handler; void *arg; /* 检查释放已收到的无序报文的资源,提高资源空闲空间 */ PBUF_CHECK_FREE_OOSEQ(); tmptimeout = next_timeout; if (tmptimeout == NULL) { /* 没有事件就直接返回 */ return; } if (TIME_LESS_THAN(now, tmptimeout->time)) { /* 没有到期事件也不要处理 */ return; } /* 处理已超时事件 */ next_timeout = tmptimeout->next; /* 先从超时链表中移除 */ handler = tmptimeout->h; /* 获取回调函数 */ arg = tmptimeout->arg; /* 获取回调函数参数 */ current_timeout_due_time = tmptimeout->time; /* 获取当前时间 */#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES if (handler != NULL) { LWIP_DEBUGF(TIMERS_DEBUG, ("sct calling h=%s t=%"U32_F" arg=%p\n", tmptimeout->handler_name, sys_now() - tmptimeout->time, arg)); }#endif /* LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES */ /* 先释放内存资源 */ memp_free(MEMP_SYS_TIMEOUT, tmptimeout); if (handler != NULL) { handler(arg); /* 执行回调 */ } LWIP_TCPIP_THREAD_ALIVE(); /* 该宏函数默认为空。其作用是用于类似看门狗的功能 */ } while (1);}就是超时链表首节点的唤醒时间从时间轴上移到当前时间,后续节点按差跟上。
/** Rebase the timeout times to the current time. * This is necessary if sys_check_timeouts() hasn't been called for a long * time (e.g. while saving energy) to prevent all timer functions of that * period being called. */voidsys_restart_timeouts(void){ u32_t now; u32_t base; struct sys_timeo *t; if (next_timeout == NULL) { return; } now = sys_now(); base = next_timeout->time; /* 获取超时链表首节点唤醒时间 */ for (t = next_timeout; t != NULL; t = t->next) { /* 把超时链表上的所有事件的唤醒时间在时间轴上前移(base-now)个单位 */ t->time = (t->time - base) + now; }}/* 返回下一次超时到期前的剩余时间。如果没有加入超时队列,则返回SYS_TIMEOUTS_SLEEPTIME_INFINITE */u32_tsys_timeouts_sleeptime(void){ u32_t now; /* 确保在tcpip线程安全锁内 */ LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED(); if (next_timeout == NULL) { return SYS_TIMEOUTS_SLEEPTIME_INFINITE; } now = sys_now(); if (TIME_LESS_THAN(next_timeout->time, now)) { /* 已经有事件到期了,返回0 */ return 0; } else { u32_t ret = (u32_t)(next_timeout->time - now); /* 返回现在到下次唤醒的剩余时间 */ LWIP_ASSERT("invalid sleeptime", ret <= LWIP_MAX_TIMEOUT); /* 差值不能超过LWIP_MAX_TIMEOUT */ return ret; }}周期定时机制基于内核超时机制。
利用lwip_cyclic_timer()做超时函数:
周期定时机制的数据结构:
/* lwip周期定时机制数据结构 */struct lwip_cyclic_timer { u32_t interval_ms; /* 周期值 */ lwip_cyclic_timer_handler handler; /* 回调函数 */#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES const char* handler_name; /* 周期定时事件文本描述 */#endif /* LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES */};周期定时机制的基函数:
/** * 定时器回调函数,调用循环>处理程序()并重新调度自己 * * @param arg unused argument */#if !LWIP_TESTMODEstatic#endifvoidlwip_cyclic_timer(void *arg){ u32_t now; u32_t next_timeout_time; /* 超时事件的回调参数就是周期定时事件 */ const struct lwip_cyclic_timer *cyclic = (const struct lwip_cyclic_timer *)arg;#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES LWIP_DEBUGF(TIMERS_DEBUG, ("tcpip: %s()\n", cyclic->handler_name));#endif cyclic->handler(); /* 执行周期定时回调函数 */ now = sys_now(); /* 获取当前时间 */ /* 计算下一个唤醒当前周期定时事件的时间,应该从上一个理应唤醒时间开始计 */ next_timeout_time = (u32_t)(current_timeout_due_time + cyclic->interval_ms); if (TIME_LESS_THAN(next_timeout_time, now)) { /* 如果当前定时事件的下一个唤醒时间也过期了,那就重新计时,以当前时间为基准 */#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES sys_timeout_abs((u32_t)(now + cyclic->interval_ms), lwip_cyclic_timer, arg, cyclic->handler_name);#else /* 重新插入到超时链表,实现周期定时回调 */ sys_timeout_abs((u32_t)(now + cyclic->interval_ms), lwip_cyclic_timer, arg);#endif } else { /* 下一个唤醒时间还没到期 */#if LWIP_DEBUG_TIMERNAMES sys_timeout_abs(next_timeout_time, lwip_cyclic_timer, arg, cyclic->handler_name);#else /* 重新插入到超时链表,实现周期定时回调 */ sys_timeout_abs(next_timeout_time, lwip_cyclic_timer, arg);#endif }}lwip消息就是其它线程把业务外包到lwip内核主线程tcpip_thread()去执行。
LwIP中必须存在的消息,整个内核的运作都要依赖他们:
因为lwip中有多种消息类型,所以数据结构使用联合体。
struct tcpip_msg { enum tcpip_msg_type type; /* msg类型 */ union {#if !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING struct { tcpip_callback_fn function; /* 需要内核执行的API */ void* msg; /* API的参数指针,内含多个参数 */ } api_msg; /* TCPIP_MSG_API。API消息 */ struct { tcpip_api_call_fn function; /* 需要内核执行的API */ struct tcpip_api_call_data *arg; sys_sem_t *sem; } api_call; /* TCPIP_MSG_API_CALL。API回传消息 */#endif /* LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING */#if !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT struct { struct pbuf *p; /* 收到的数据包 */ struct netif *netif; /* 来自哪个网卡的 */ netif_input_fn input_fn; /* 需要传入哪个内核函数处理 */ } inp; /* TCPIP_MSG_INPKT。网络数据包消息 */#endif /* !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT */ struct { tcpip_callback_fn function; void *ctx; } cb; /* TCPIP_MSG_CALLBACK、TCPIP_MSG_CALLBACK_STATIC。回调消息 */#if LWIP_TCPIP_TIMEOUT && LWIP_TIMERS struct { u32_t msecs; sys_timeout_handler h; void *arg; } tmo; /* TCPIP_MSG_TIMEOUT、TCPIP_MSG_UNTIMEOUT。注册注销超时消息 */#endif /* LWIP_TCPIP_TIMEOUT && LWIP_TIMERS */ } msg;};enum tcpip_msg_type {#if !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING TCPIP_MSG_API, /* API消息类型。如用户调用应用层的接口时,需要tcpip_thread执行内核函数就用这个消息类型。需要往南供给协议栈。 */ TCPIP_MSG_API_CALL, /* API回传消息类型。比如用户调用应用层有回传的接口时,就用这个消息类型。需要往南供给协议栈。 */#endif /* !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING */#if !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT TCPIP_MSG_INPKT, /* 网络数据包消息类型。即是网卡上收到的数据。需要往北供给协议栈。 */#endif /* !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT */#if LWIP_TCPIP_TIMEOUT && LWIP_TIMERS TCPIP_MSG_TIMEOUT, /* 注册超时定时器消息类型。 */ TCPIP_MSG_UNTIMEOUT, /* 注销超时定时器消息类型。 */#endif /* LWIP_TCPIP_TIMEOUT && LWIP_TIMERS */ TCPIP_MSG_CALLBACK, /* 回调消息类型。就是让tcpip_thread这个线程帮忙执行这个回调函数,这个回调函数就能肆无忌惮地访问内核函数了。 */ TCPIP_MSG_CALLBACK_STATIC /* 静态的回调消息类型。 */};API消息是有用户线程发出,与内核进行交互。
用户调用应用层接口,往南执行协议栈内核函数,需要tcpip_thread线程执行时,通过API消息告知tcpip_thread线程执行。
在线程间通信中的api消息类型对应的数据结构伪代码如下:
struct { tcpip_callback_fn function; /* 需要内核执行的API */ void* msg; /* API的参数指针,内含多个参数 */ } api_msg; /* TCPIP_MSG_API。API消息 */其中,void* msg;这个参数才是真正的API消息数据结构,对应是struct api_msg。
要注意区分,前者是用于线程间通信的API消息的数据结构。后者是API消息内容的数据结构。
struct api_msg包含3个字段:
struct netconn *conn;err_t err;union msg;struct api_msg:
/* IP addresses and port numbers are expected to be in the same byte order as in the corresponding pcb. *//* 这个数据结构包含了在另一个线程上下文中执行netconn函数所需的所有内容(主要用于处理tcpip_thread上下文中的netconn以确保线程安全)。 */struct api_msg { /* 当前需要执行的API对应的连接 */ struct netconn *conn; /* 在tcpip_thread中执行的函数的返回值 */ err_t err; /* 用户调用不同的API,会使用不同的数据结构 */ union { /* used for lwip_netconn_do_send */ struct netbuf *b; /** used for lwip_netconn_do_newconn */ struct { u8_t proto; } n; /** used for lwip_netconn_do_bind and lwip_netconn_do_connect */ struct { API_MSG_M_DEF_C(ip_addr_t, ipaddr); u16_t port; u8_t if_idx; } bc; /** used for lwip_netconn_do_getaddr */ struct { ip_addr_t API_MSG_M_DEF(ipaddr); u16_t API_MSG_M_DEF(port); u8_t local; } ad; /** used for lwip_netconn_do_write */ struct { /** current vector to write */ const struct netvector *vector; /** number of unwritten vectors */ u16_t vector_cnt; /** offset into current vector */ size_t vector_off; /** total length across vectors */ size_t len; /** offset into total length/output of bytes written when err == ERR_OK */ size_t offset; u8_t apiflags;#if LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO u32_t time_started;#endif /* LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO */ } w; /* used for lwip_netconn_do_recv */ struct { size_t len; } r;#if LWIP_TCP /* used for lwip_netconn_do_close (/shutdown) */ struct { u8_t shut;#if LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO || LWIP_SO_LINGER u32_t time_started;#else /* LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO || LWIP_SO_LINGER */ u8_t polls_left;#endif /* LWIP_SO_SNDTIMEO || LWIP_SO_LINGER */ } sd;#endif /* LWIP_TCP */#if LWIP_IGMP || (LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_IPV6_MLD) /* used for lwip_netconn_do_join_leave_group */ struct { API_MSG_M_DEF_C(ip_addr_t, multiaddr); API_MSG_M_DEF_C(ip_addr_t, netif_addr); u8_t if_idx; enum netconn_igmp join_or_leave; } jl;#endif /* LWIP_IGMP || (LWIP_IPV6 && LWIP_IPV6_MLD) */#if TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG struct { u8_t backlog; } lb;#endif /* TCP_LISTEN_BACKLOG */ } msg;#if LWIP_NETCONN_SEM_PER_THREAD sys_sem_t* op_completed_sem;#endif /* LWIP_NETCONN_SEM_PER_THREAD */};待画:后续分析完socket API源码实现后再补上
消息类型为TCPIP_MSG_INPKT。
数据包消息是底层网卡接收到数据后需要往北交给协议栈处理时需要构造的消息。
在tcpip_inpkt()函数中构造。
主要将收到的数据包传递到tcpip_thread线程执行。并告知要传入哪个内核函数处理。
tcpip_inpkt():
实现分两种:
tcpip_thread处理。/** * 将接收到的数据包打包给tcpip_thread执行 * * @param p the received packet * @param inp the network interface on which the packet was received * @param input_fn input function to call */err_ttcpip_inpkt(struct pbuf *p, struct netif *inp, netif_input_fn input_fn){#if LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT /* 开放了tcpip内核锁给input业务处理,就不需要外包到tcpip_thread处理 */ err_t ret; LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_inpkt: PACKET %p/%p\n", (void *)p, (void *)inp)); LOCK_TCPIP_CORE(); /* 获取tcpip内核锁 */ ret = input_fn(p, inp); /* 直接在本线程处理收到的数据包 */ UNLOCK_TCPIP_CORE(); /* 释放tcpip内核锁 */ return ret;#else /* 如果没有开放tcpip内核锁给input业务处理,就需要外包到tcpip_thread处理 */ struct tcpip_msg *msg; LWIP_ASSERT("Invalid mbox", sys_mbox_valid_val(tcpip_mbox)); /* 申请数据包消息资源 */ msg = (struct tcpip_msg *)memp_malloc(MEMP_TCPIP_MSG_INPKT); if (msg == NULL) { return ERR_MEM; } /* 配置消息 */ msg->type = TCPIP_MSG_INPKT; /* 数据包消息类型 */ msg->msg.inp.p = p; msg->msg.inp.netif = inp; msg->msg.inp.input_fn = input_fn; if (sys_mbox_trypost(&tcpip_mbox, msg) != ERR_OK) { /* 投递消息,非阻塞 */ memp_free(MEMP_TCPIP_MSG_INPKT, msg); /* 投递失败,释放资源 */ return ERR_MEM; } return ERR_OK;#endif /* LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT */}lwip数据包南向收包流图:

LwIP内核是作为操作系统的一个线程运行的,在协议栈初始化的时候就会创建tcpip_thread线程。
该线程主要处理超时检查和接收各种消息进行处理。
tcpip内核锁是维护tcpip内核函数的原子性。
tcpip_thread内核线程和其它线程对内核tcpip的函数存在竞争关系。
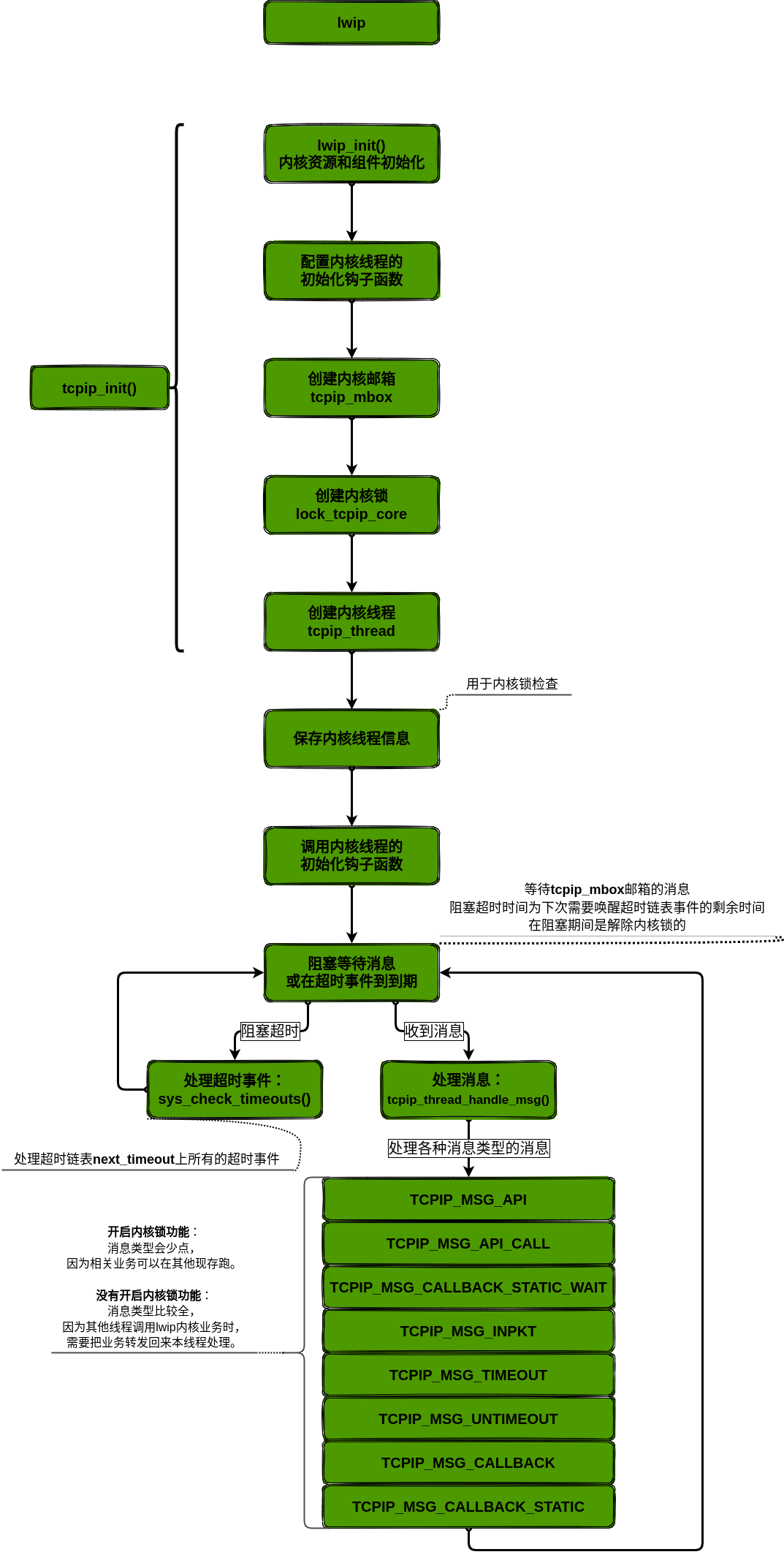
lwIP主线程。
这个线程独占地访问lwIP核心函数(除非对它们的访问没有被锁定)。
其他线程使用消息框与该线程通信。
该线程还启动所有计时器,以确保它们在正确的线程上下文中运行。
/** * The main lwIP thread. This thread has exclusive access to lwIP core functions (unless access to them is not locked). Other threads communicate with this thread using message boxes. * * It also starts all the timers to make sure they are running in the right thread context. * * @param arg unused argument */static voidtcpip_thread(void *arg){ struct tcpip_msg *msg; LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg); /* 记录当前线程 */ LWIP_MARK_TCPIP_THREAD(); /* tcpip内核上锁 */ LOCK_TCPIP_CORE(); if (tcpip_init_done != NULL) { /* 执行用户插入的lwip内核初始化钩子函数 */ tcpip_init_done(tcpip_init_done_arg); } while (1) { /* MAIN Loop */ LWIP_TCPIP_THREAD_ALIVE(); /* 默认为空。这个可用于类似看门狗功能 */ /* 等待消息或超时事件 */ TCPIP_MBOX_FETCH(&tcpip_mbox, (void **)&msg); if (msg == NULL) { LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: invalid message: NULL\n")); LWIP_ASSERT("tcpip_thread: invalid message", 0); continue; /* 没有消息,继续等待 */ } /* 处理收到的消息 */ tcpip_thread_handle_msg(msg); }}#if !LWIP_TIMERS/* 只等待消息 */#define TCPIP_MBOX_FETCH(mbox, msg) sys_mbox_fetch(mbox, msg)#else /* !LWIP_TIMERS *//* 等待消息或超时事件 */#define TCPIP_MBOX_FETCH(mbox, msg) tcpip_timeouts_mbox_fetch(mbox, msg)/** * 永久等待一个消息,在等待过程中如果有超时事件发生,也会处理超时事件 * * @param mbox the mbox to fetch the message from * @param msg the place to store the message */static voidtcpip_timeouts_mbox_fetch(sys_mbox_t *mbox, void **msg){ u32_t sleeptime, res;again: /* 确保当前在tcpip内核锁内 */ LWIP_ASSERT_CORE_LOCKED(); /* 获取下一个需要唤醒的超时事件的剩余时间 */ sleeptime = sys_timeouts_sleeptime(); if (sleeptime == SYS_TIMEOUTS_SLEEPTIME_INFINITE) { /* 没有超时事件在等待 */ /* 释放tcpip内核锁 */ UNLOCK_TCPIP_CORE(); /* 永久等待消息 */ sys_arch_mbox_fetch(mbox, msg, 0); /* 拿到消息后,tcpip内核上锁 */ LOCK_TCPIP_CORE(); return; } else if (sleeptime == 0) { /* 如果有事件超时了,就先处理超时事件 */ sys_check_timeouts(); /* 处理所有超时了的事件 */ /* 处理完毕后继续等待消息或超时事件 */ goto again; } /* 如果没有消息,且存在超时事件在计时,就按需休眠 */ /* 释放tcpip内核锁 */ UNLOCK_TCPIP_CORE(); /* 等待消息,直至有消息到来或者有超时事件需要唤醒处理,才解除阻塞 */ res = sys_arch_mbox_fetch(mbox, msg, sleeptime); /* 有消息或者事件需要处理时,进入tcpip内核锁 */ LOCK_TCPIP_CORE(); if (res == SYS_ARCH_TIMEOUT) { /* 如果等待消息超时了,说明超时链表中有超时事件需要唤醒了 */ sys_check_timeouts(); /* 处理所有超时了的事件 */ /* 处理完毕后继续等待消息或超时事件 */ goto again; }}#endif /* !LWIP_TIMERS */其它线程需要发消息到tcpip_thread()线程来处理内核操作。
如果开启了tcpip内核锁,客户端对lwip的操作也可以不用外包tcpip_thread()线程处理。
/* 处理单个tcpip_msg * This is in its own function for access by tests only. */static voidtcpip_thread_handle_msg(struct tcpip_msg *msg){ switch (msg->type) {#if !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING /* 没有开启tcpip内核锁,其它线程对lwip的操作需要外包到tcpip_thread线程操作 */ case TCPIP_MSG_API: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: API message %p\n", (void *)msg)); msg->msg.api_msg.function(msg->msg.api_msg.msg); /* 执行API */ break; case TCPIP_MSG_API_CALL: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: API CALL message %p\n", (void *)msg)); msg->msg.api_call.arg->err = msg->msg.api_call.function(msg->msg.api_call.arg); /* 执行API,并返回结果码 */ sys_sem_signal(msg->msg.api_call.sem); /* 释放信号量,告知用户线程执行API完毕 */ break; case TCPIP_MSG_CALLBACK_STATIC_WAIT: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: CALLBACK WAIT message %p\n", (void *)msg)); msg->msg.cb_wait.function(msg->msg.cb_wait.ctx); /* 执行回调 */ sys_sem_signal(msg->msg.cb_wait.sem); /* 释放信号量,告知插入回调的线程回调执行完毕 */ break;#endif /* !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING */#if !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT /* 没有开启LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT,所以tcpip_input()没有权限好的tcpip内核锁,只能外包回tcpip_tread线程处理 */ case TCPIP_MSG_INPKT: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: PACKET %p\n", (void *)msg)); if (msg->msg.inp.input_fn(msg->msg.inp.p, msg->msg.inp.netif) != ERR_OK) { /* 处理收到的数据包 */ pbuf_free(msg->msg.inp.p); /* 处理完毕后释放这个pbuf的资源 */ } memp_free(MEMP_TCPIP_MSG_INPKT, msg); /* 释放消息资源 */ break;#endif /* !LWIP_TCPIP_CORE_LOCKING_INPUT */#if LWIP_TCPIP_TIMEOUT && LWIP_TIMERS /* 支持在tcpip_thread执行计时器功能 */ case TCPIP_MSG_TIMEOUT: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: TIMEOUT %p\n", (void *)msg)); sys_timeout(msg->msg.tmo.msecs, msg->msg.tmo.h, msg->msg.tmo.arg); /* 注册超时事件 */ memp_free(MEMP_TCPIP_MSG_API, msg); /* 释放消息资源 */ break; case TCPIP_MSG_UNTIMEOUT: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: UNTIMEOUT %p\n", (void *)msg)); sys_untimeout(msg->msg.tmo.h, msg->msg.tmo.arg); /* 注销超时事件 */ memp_free(MEMP_TCPIP_MSG_API, msg); /* 释放消息资源 */ break;#endif /* LWIP_TCPIP_TIMEOUT && LWIP_TIMERS */ case TCPIP_MSG_CALLBACK: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: CALLBACK %p\n", (void *)msg)); msg->msg.cb.function(msg->msg.cb.ctx); /* 执行回调 */ memp_free(MEMP_TCPIP_MSG_API, msg); /* 释放消息资源 */ break; case TCPIP_MSG_CALLBACK_STATIC: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: CALLBACK_STATIC %p\n", (void *)msg)); msg->msg.cb.function(msg->msg.cb.ctx); /* 执行回调。静态,不需要释放消息资源 */ break; default: LWIP_DEBUGF(TCPIP_DEBUG, ("tcpip_thread: invalid message: %d\n", msg->type)); LWIP_ASSERT("tcpip_thread: invalid message", 0); break; }}后续分析完socket API源码实现后再补上(还有最后一层 socket API源码实现还没分析,所以全局数据库流图还有一层未画)