题外话
"行百里者半九十",是说步行一百里路,走过九十里,只能算是走了一半。因为步行越接近目的地,走起来越困难。借指凡事到了接近成功,往往是最吃力、最艰难的时段。劝人做事贵在坚持,有始容易,有终实难。
不多说了,希望自己能坚持写完这个系列 ......
在前几篇文章中,你应该已经看到文中有冒出来比较多的陌生的类,比如 Surface/SurfaceControl/ANativeWindow/ANativeWindowBuffer,这些类有什么作用?它们之间有什么关系?以及它们和BufferQueue之间的关系是怎样的?我们带着这些问题,来开始这篇文章的讲解
? ANativeWindow
? Surface
? SurfaceControl
? ANativeWindowBuffer
ANativeWindow 顾名思义,这个结构体是对一个本地窗口的抽象描述。老规矩先看代码:
其定义位于:/frameworks/native/libs/nativewindow/include/system/window.h
struct ANativeWindow{ // C++ 代码下会定义构造函数,并初始化common成员中的部分信息#ifdef __cplusplus ANativeWindow() : flags(0), minSwapInterval(0), maxSwapInterval(0), xdpi(0), ydpi(0) { common.magic = ANDROID_NATIVE_WINDOW_MAGIC; common.version = sizeof(ANativeWindow); memset(common.reserved, 0, sizeof(common.reserved)); } /* Implement the methods that sp<ANativeWindow> expects so that it can be used to automatically refcount ANativeWindow's. */ void incStrong(const void* /*id*/) const { common.incRef(const_cast<android_native_base_t*>(&common)); } void decStrong(const void* /*id*/) const { common.decRef(const_cast<android_native_base_t*>(&common)); }#endif // 结构体第一个成员,相当于继承自android_native_base_t,其主要用于引用计数,还有版本信息 struct android_native_base_t common; /* flags describing some attributes of this surface or its updater */ const uint32_t flags; /* min swap interval supported by this updated */ const int minSwapInterval; /* max swap interval supported by this updated */ const int maxSwapInterval; /* horizontal and vertical resolution in DPI */ const float xdpi; const float ydpi; /* Some storage reserved for the OEM's driver. */ intptr_t oem[4]; /* 设置swap间隔,跟踪源码可发现其最终调用了mGraphicBufferProducer->setAsyncMode, 也就是设置Producer是同步or异步模式 */ int (*setSwapInterval)(struct ANativeWindow* window, int interval); /* 请求(出队列)一块buffer。执行后这块buffer就不是locked锁定状态,因此内容不能被修改。 如果没有可用的buffer,这个方法会被阻塞。 该方法已被弃用。*/ int (*dequeueBuffer_DEPRECATED)(struct ANativeWindow* window, struct ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer); /* 锁住buffer。在修改buffer中的内容前一定要先调用lock方法。 这块buffer首先是dequeueBuffer请求到的。 该方法已被弃用。*/ */ int (*lockBuffer_DEPRECATED)(struct ANativeWindow* window, struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer); /* 当修改完buffer内容,调用这个方法,把buffer返回到队列中,用于后续显示输出。 该方法已被弃用。*/ int (*queueBuffer_DEPRECATED)(struct ANativeWindow* window, struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer); /* 检索查询有关 native window 的信息 what指明要查询信息的类型,比如 NATIVE_WINDOW_WIDTH 、NATIVE_WINDOW_HEIGHT 查询宽高*/ int (*query)(const struct ANativeWindow* window, int what, int* value); /* 对surface执行各种操作,比如 NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_USAGE or NATIVE_WINDOW_CONNECT 一般不会直接调用这个方法,而是使用辅助方法,比如 native_window_set_usage */ int (*perform)(struct ANativeWindow* window, int operation, ... ); /* 取消已出队列的buffer。这个方法已被弃用 */ int (*cancelBuffer_DEPRECATED)(struct ANativeWindow* window, struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer); /* 请求(出队列)一块buffer。如果没有可用的buffer,这个方法会被阻塞。 fenceFd是一个fence文件描述符,可以简单理解为一个资源同步锁 当发出fence信号后才可以写buffer */ int (*dequeueBuffer)(struct ANativeWindow* window, struct ANativeWindowBuffer** buffer, int* fenceFd); /* 入队列一块buffer */ int (*queueBuffer)(struct ANativeWindow* window, struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd); /* 取消一块已经dequeue的buffer */ int (*cancelBuffer)(struct ANativeWindow* window, struct ANativeWindowBuffer* buffer, int fenceFd);};在/frameworks/native/libs/nativewindow/include/system/window.h这个头文件中,还定义很多enum常量,这些常量的作用这源码中都有详细的英文注释,建议直接阅读理解。
用于query()函数检索信息的常量
/* attributes queriable with query() */enum { NATIVE_WINDOW_WIDTH = 0, NATIVE_WINDOW_HEIGHT = 1, NATIVE_WINDOW_FORMAT = 2, NATIVE_WINDOW_MIN_UNDEQUEUED_BUFFERS = ANATIVEWINDOW_QUERY_MIN_UNDEQUEUED_BUFFERS, NATIVE_WINDOW_QUEUES_TO_WINDOW_COMPOSER = 4, NATIVE_WINDOW_CONCRETE_TYPE = 5, NATIVE_WINDOW_DEFAULT_WIDTH = ANATIVEWINDOW_QUERY_DEFAULT_WIDTH, NATIVE_WINDOW_DEFAULT_HEIGHT = ANATIVEWINDOW_QUERY_DEFAULT_HEIGHT, NATIVE_WINDOW_TRANSFORM_HINT = ANATIVEWINDOW_QUERY_TRANSFORM_HINT, NATIVE_WINDOW_CONSUMER_RUNNING_BEHIND = 9, NATIVE_WINDOW_CONSUMER_USAGE_BITS = 10, /* deprecated */ NATIVE_WINDOW_STICKY_TRANSFORM = 11, NATIVE_WINDOW_DEFAULT_DATASPACE = 12, NATIVE_WINDOW_BUFFER_AGE = ANATIVEWINDOW_QUERY_BUFFER_AGE, NATIVE_WINDOW_LAST_DEQUEUE_DURATION = 14, NATIVE_WINDOW_LAST_QUEUE_DURATION = 15, NATIVE_WINDOW_LAYER_COUNT = 16, NATIVE_WINDOW_IS_VALID = 17, NATIVE_WINDOW_FRAME_TIMESTAMPS_SUPPORTS_PRESENT = 18, NATIVE_WINDOW_CONSUMER_IS_PROTECTED = 19, NATIVE_WINDOW_DATASPACE = 20, NATIVE_WINDOW_MAX_BUFFER_COUNT = 21,};用于(*perform)()的标识各种操作的常量
deprecated标记的可能已被弃用或被其他功能函数取代
标记为“私有”的值应被视为框架私有。可以访问ANativeWindow的HAL实现代码不应该使用这些,因为它可能无法与框架对ANativeWindow的使用进行正确的交互。
/* Valid operations for the (*perform)() hook. */enum { // clang-format off NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_USAGE = ANATIVEWINDOW_PERFORM_SET_USAGE, /* deprecated */ NATIVE_WINDOW_CONNECT = 1, /* deprecated */ NATIVE_WINDOW_DISCONNECT = 2, /* deprecated */ NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_CROP = 3, /* private */ // 完整内容,请参考源码 }用于NATIVE_WINDOW_[API_][DIS]CONNECT的参数
两个函数native_window_api_connect 和 native_window_api_disconnect
/* parameter for NATIVE_WINDOW_[API_][DIS]CONNECT */enum { NATIVE_WINDOW_API_EGL = 1, // 使用OpenGL ES填充buffer后,EGL通过eglSwapBuffers入队列这个buffer NATIVE_WINDOW_API_CPU = 2, // 使用CPU填充buffer后,入队列buffer NATIVE_WINDOW_API_MEDIA = 3, // video解码器填充buffer后,Stagefright入队列这个buffer NATIVE_WINDOW_API_CAMERA = 4,// 友camera HAL 入队列buffer};用于NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_BUFFERS_TRANSFORM 图像转换的参数
/* parameter for NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_BUFFERS_TRANSFORM */enum { NATIVE_WINDOW_TRANSFORM_FLIP_H = HAL_TRANSFORM_FLIP_H ,// 水平翻转 NATIVE_WINDOW_TRANSFORM_FLIP_V = HAL_TRANSFORM_FLIP_V, // 垂直翻转 NATIVE_WINDOW_TRANSFORM_ROT_90 = HAL_TRANSFORM_ROT_90, // 将源图像按时钟方向旋转90度 NATIVE_WINDOW_TRANSFORM_ROT_180 = HAL_TRANSFORM_ROT_180,// 将源图像按时钟方向旋转180度 NATIVE_WINDOW_TRANSFORM_ROT_270 = HAL_TRANSFORM_ROT_270, // 将源图像按时钟方向旋转270度 NATIVE_WINDOW_TRANSFORM_INVERSE_DISPLAY = 0x08 // 通过对其显示的屏幕进行逆变换来转换源。};上述参数即用于如下这个函数,buffer显示时就会按照我们设置的转换类型进行翻转、旋转。
/* * native_window_set_buffers_transform(..., int transform) * All buffers queued after this call will be displayed transformed according * to the transform parameter specified. */static inline int native_window_set_buffers_transform( struct ANativeWindow* window, int transform){ return window->perform(window, NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_BUFFERS_TRANSFORM, transform);}用于NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_SCALING_MODE设置缩放模式的常量
/* parameter for NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_SCALING_MODE */enum { /* the window content is not updated (frozen) until a buffer of * the window size is received (enqueued) */ NATIVE_WINDOW_SCALING_MODE_FREEZE = 0, /* the buffer is scaled in both dimensions to match the window size */ NATIVE_WINDOW_SCALING_MODE_SCALE_TO_WINDOW = 1, /* the buffer is scaled uniformly such that the smaller dimension * of the buffer matches the window size (cropping in the process) */ NATIVE_WINDOW_SCALING_MODE_SCALE_CROP = 2, /* the window is clipped to the size of the buffer's crop rectangle; pixels * outside the crop rectangle are treated as if they are completely * transparent. */ NATIVE_WINDOW_SCALING_MODE_NO_SCALE_CROP = 3,};上述参数即用于如下这个函数
/* * native_window_set_scaling_mode(..., int mode) * All buffers queued after this call will be associated with the scaling mode * specified. */static inline int native_window_set_scaling_mode( struct ANativeWindow* window, int mode){ return window->perform(window, NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_SCALING_MODE, mode);}
Surface和ANativeWindow存在千丝万缕的联系,Surface继承了ANativeWindow,并对其中的功能做了具体实现。
ANativeWindow这个结构体中定义了大量的函数指针,这些函数指针指向了哪里?或函数功能在哪里?答案就在Surface中。
Surface的定义位于:/frameworks/native/libs/gui/include/gui/Surface.h
先看看它的声明:
class Surface : public ANativeObjectBase<ANativeWindow, Surface, RefBase>{ ......}ANativeObjectBase是一个模板类,作为辅助类将ANativeXXXX的对象类型转换为C++的引用计数类型
template <typename NATIVE_TYPE, typename TYPE, typename REF, typename NATIVE_BASE = android_native_base_t>class ANativeObjectBase : public NATIVE_TYPE, public REF{我们结合上面这两段代码来看,是不是很清晰了:
在Surface的定义中,NATIVE_TYPE==ANativeWindow , REF==RefBas ==> ANativeObjectBase 继承了ANativeWindow
根据继承的逻辑关系,很明显Surface继承了ANativeWindow
Surface中定义了很多函数接口,不过也有些规律。
? hook_*的函数
hook函数有10个,这些函数和ANativeWindow中定义的函数指针对应,hook钩连一块
他们是怎么样钩连起来的呢?可以看/frameworks/native/libs/gui/Surface.cpp 中构造函数
Surface::Surface(const sp<IGraphicBufferProducer>& bufferProducer, bool controlledByApp, const sp<IBinder>& surfaceControlHandle) : .... { // Initialize the ANativeWindow function pointers. ANativeWindow::setSwapInterval = hook_setSwapInterval; ANativeWindow::dequeueBuffer = hook_dequeueBuffer; ANativeWindow::cancelBuffer = hook_cancelBuffer; ANativeWindow::queueBuffer = hook_queueBuffer; ANativeWindow::query = hook_query; ANativeWindow::perform = hook_perform; ANativeWindow::dequeueBuffer_DEPRECATED = hook_dequeueBuffer_DEPRECATED; ANativeWindow::cancelBuffer_DEPRECATED = hook_cancelBuffer_DEPRECATED; ANativeWindow::lockBuffer_DEPRECATED = hook_lockBuffer_DEPRECATED; ANativeWindow::queueBuffer_DEPRECATED = hook_queueBuffer_DEPRECATED;}一目了然,Initialize the ANativeWindow function pointers. 初始化函数指针。
比如我们程序中如果调用ANativeWindow::query函数,即会调用实现具体功能的Surface::hook_query.
? dispatch*的函数
dispatch函数有46个,前面我们有讲到perform函数对应的各种操作,都是会走到对应的dispatch函数中。
我们通过一个例子来说明下具体流程:Android 12(S) 图形显示系统 - 示例应用(二)
之前的demo中 ,比如有用到
// 3. set the ANativeWindow format err = native_window_set_buffers_format(nativeWindow, PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBX_8888);看!native_window_set_buffers_format的定义
static inline int native_window_set_buffers_format( struct ANativeWindow* window, int format){ return window->perform(window, NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_BUFFERS_FORMAT, format);}其中继续调用 window->perform(),这个函数对应到了Surface::hook_perform
int Surface::hook_perform(ANativeWindow* window, int operation, ...) { va_list args; va_start(args, operation); Surface* c = getSelf(window); // 类型转换 int result; // Don't acquire shared ownership of the interceptor mutex if we're going to // do interceptor registration, as otherwise we'll deadlock on acquiring // exclusive ownership. if (!isInterceptorRegistrationOp(operation)) { std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(c->mInterceptorMutex); if (c->mPerformInterceptor != nullptr) { result = c->mPerformInterceptor(window, Surface::performInternal, c->mPerformInterceptorData, operation, args); va_end(args); return result; } } result = c->perform(operation, args); va_end(args); return result;}接着看! 调用c->perform(),流程到了Surface::perform
int Surface::perform(int operation, va_list args){ int res = NO_ERROR; switch (operation) { ...... case NATIVE_WINDOW_SET_BUFFERS_FORMAT: res = dispatchSetBuffersFormat(args); break; ...... } }switch语句中判断是哪种case(哪中操作),调用对应的dispatchXXX,在我们的例子中即调用dispatchSetBuffersFormat
int Surface::dispatchSetBuffersFormat(va_list args) { PixelFormat format = va_arg(args, PixelFormat); return setBuffersFormat(format);}私有方法Surface::setBuffersFormat 中来完成最终的工作。
通过上面这个例子应该就理清了 perform <--> dispatchXXX 的处理流程了
? 其它的函数和私有成员
Surface中还有很多函数和数据成员,它们提供了操作surface的接口或用于存surface的属性信息。
比如 宽、高、像素格式等属性信息
BufferSlot mSlots[NUM_BUFFER_SLOTS]; uint32_t mReqWidth; uint32_t mReqHeight; PixelFormat mReqFormat; uint64_t mReqUsage;我们在此就不展开介绍了,后续讲解中如有遇到会再解释。
简单小结下:ANativeWindow中定义很多函数指针成员变量,Surface继承自ANativeWindow,当然那些函数指针成员变量也是属于Surface了,Surface实现了各种功能函数,并且让ANativeWindow中函数指针成员变量与实际功能函数建立关联(hook)
window.h中有很多static函数,使用这些函数时就可以透过ANativeWindow呼叫到Surface中的功能了
绕啊绕,绕啊绕,为啥要这样绕....
SurfaceControl 顾名思义是用于控制surface的一个类。他是如何进行控制的呢?且让我们慢慢看....
还记得我们例子中如何创建surface的吗?可以回头再看看 Android 12(S) 图形显示系统 - 示例应用(二)
使用SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface 获得了SurfaceControl对象,神奇吧!
sp<SurfaceControl> surfaceControl = surfaceComposerClient->createSurface(mName, resolution.getWidth(), resolution.getHeight(), PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888, ISurfaceComposerClient::eFXSurfaceBufferState, /*parent*/ nullptr);深入其中,一探究竟,createSurface做了什么神奇操作呢?
sp<SurfaceControl> SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface(const String8& name, uint32_t w, uint32_t h, PixelFormat format, uint32_t flags, const sp<IBinder>& parentHandle, LayerMetadata metadata, uint32_t* outTransformHint) { sp<SurfaceControl> s; createSurfaceChecked(name, w, h, format, &s, flags, parentHandle, std::move(metadata), outTransformHint); return s;}继续去调用 createSurfaceChecked
status_t SurfaceComposerClient::createSurfaceChecked(const String8& name, uint32_t w, uint32_t h, PixelFormat format, sp<SurfaceControl>* outSurface, uint32_t flags, const sp<IBinder>& parentHandle, LayerMetadata metadata, uint32_t* outTransformHint) { sp<SurfaceControl> sur; status_t err = mStatus; if (mStatus == NO_ERROR) { sp<IBinder> handle; sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> gbp; uint32_t transformHint = 0; int32_t id = -1; err = mClient->createSurface(name, w, h, format, flags, parentHandle, std::move(metadata), &handle, &gbp, &id, &transformHint); if (outTransformHint) { *outTransformHint = transformHint; } ALOGE_IF(err, "SurfaceComposerClient::createSurface error %s", strerror(-err)); if (err == NO_ERROR) { *outSurface = new SurfaceControl(this, handle, gbp, id, w, h, format, transformHint, flags); } } return err;}真相已浮现,看到 new SurfaceControl 了
在前面文章
Android 12(S) 图形显示系统 - createSurface的流程(五)Android 12(S) 图形显示系统 - BufferQueue/BLASTBufferQueue之初识(六)我们详细分析过createSurface的流程,还有SurfaceControl中的信息,我们再贴一下信息:
源码位置: /frameworks/native/libs/gui/include/gui/SurfaceControl.h
class SurfaceControl : public RefBase ...private: sp<SurfaceComposerClient> mClient; // 应用创建的SurfaceComposerClient对象指针,里面封装了和SurfaceFlinger通信的Binder客户端 sp<IBinder> mHandle; // 应用中显式创建的layer handle,这是个BufferStateLayer 它作为parent sp<IGraphicBufferProducer> mGraphicBufferProducer; // 这个貌似没有实际用了? mutable Mutex mLock; mutable sp<Surface> mSurfaceData; // mutable sp<BLASTBufferQueue> mBbq; // BLASTBufferQueue对象实例 mutable sp<SurfaceControl> mBbqChild; // child layer,它会和mBbq相关联 int32_t mLayerId; // layer id uint32_t mTransformHint; // 方向 uint32_t mWidth; // surface 宽 uint32_t mHeight; // surface 高 PixelFormat mFormat; uint32_t mCreateFlags; // createSurface的标志信息};
SurfaceControl中持有Surface:mSurfaceData, 持有BufferQueue:mBbq 这就是控制的基础
总结一张图
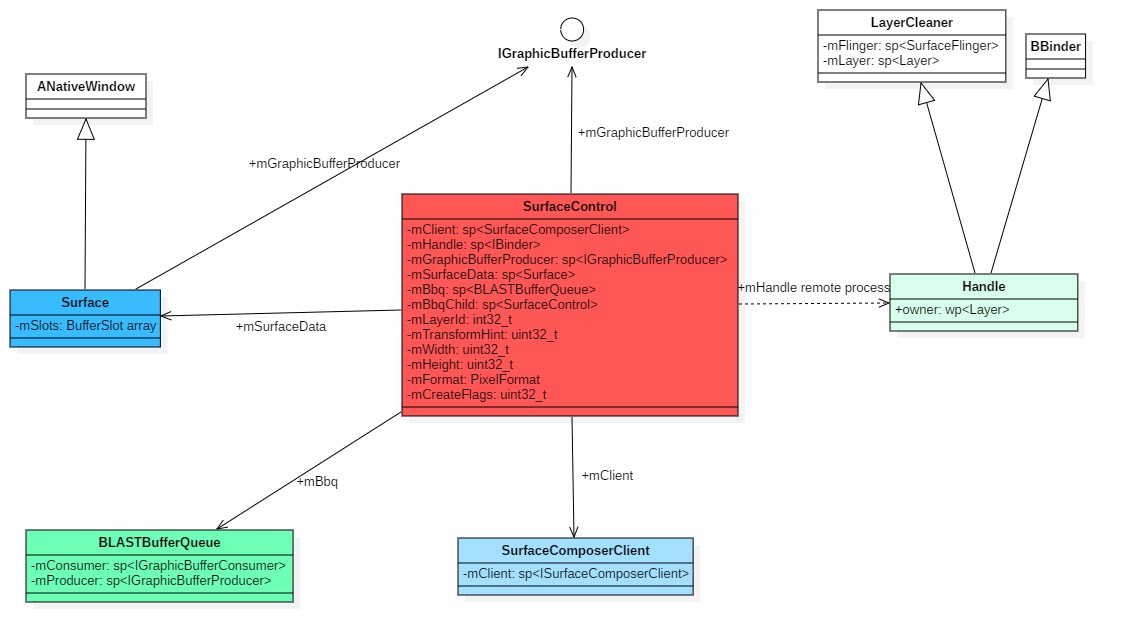
ANativeWindow/Surface/SurfaceControl的基本就介绍这些了,主要是了解这些类内有什么内容,可以使用他们做些什么操作,以及他们与其它图形组件的关系。

